Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis
What Is Eczema?
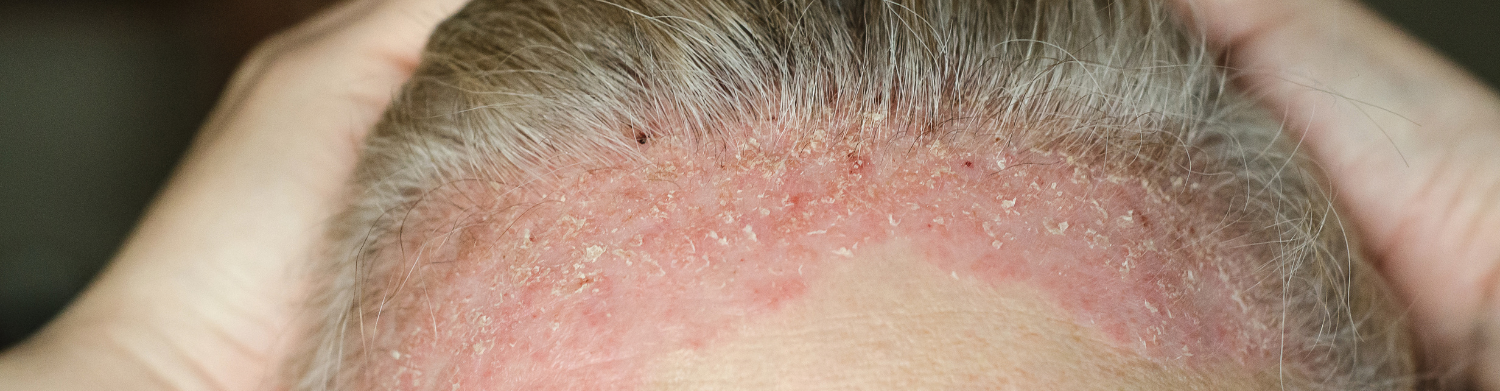
Scalp eczema involves inflammation of the skin on your scalp. It is unique due to the sensitivity and density of hair follicles in this region. The skin may become dry, flaky, or itchy, and in more severe cases, develop oozing or crusting patches.
Comparing Scalp Eczema and Psoriasis
Both scalp eczema and psoriasis cause inflamed, scaly skin. However, several characteristics set them apart:
Flaking: Seborrheic dermatitis, a type of eczema, causes oily flakes or dandruff, whereas psoriasis flakes are dry and thick.
Appearance: Psoriasis patches are well-defined, thick, and covered in silvery scales. Eczema lesions are typically red (or gray on darker skin), less clearly defined, and may ooze or crust.
Location: Scalp psoriasis often extends past the hairline and can affect other common sites like elbows and knees. Eczema tends to affect the folds of the body and may not extend beyond the scalp.
Sensation: Eczema generally causes a more intense itch, often worsening at night. On the other hand, psoriasis may include a burning or stinging sensation with a milder itch.
Age of Onset: Eczema typically starts in early childhood, while psoriasis usually begins in adolescence or adulthood.
Key Diagnostic Differences
To accurately distinguish between scalp eczema vs psoriasis, dermatologists may consider a combination of visual signs, patient history, and sometimes skin biopsies.
Visual Examination
Scalp Eczema: Usually presents as red or gray patches with white or yellow flakes. Skin may be greasy or dry, and areas might be crusted or blistered.
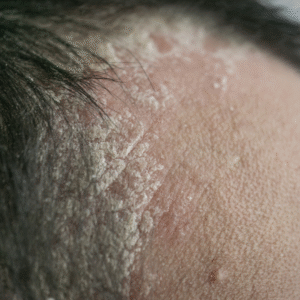
Scalp Psoriasis: Features sharply bordered plaques with thick silvery-white scales. The plaques often feel elevated and extend beyond the scalp.
Pattern and Progression
Eczema: Tends to flare with exposure to allergens or irritants and may improve with age.
Psoriasis: Typically follows a chronic course, often triggered by stress, infections, or injury to the skin.
Diagnostic Clues
Skin folds vs extensor surfaces: Eczema favors creases like behind the knees or inside elbows, while psoriasis prefers the outer surfaces.
Other signs: Nail changes (like pitting) and joint pain may hint at psoriasis.
Scalp Eczema vs Psoriasis: Treatment Approaches
Treatment for Scalp Eczema
Managing scalp eczema focuses on soothing irritation, restoring the skin barrier, and minimizing triggers.
Shampoos: Medicated products containing ingredients like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide.
Topical Treatments: Steroid creams, calcineurin inhibitors, and antifungal agents (for seborrheic dermatitis).
Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding harsh shampoos, washing with lukewarm water, and daily moisturizing.
Probiotics: Taking clinically proven probiotics that improve eczema symptoms.
Treatment for Scalp Psoriasis
Treating scalp psoriasis often requires a more aggressive approach due to the deeper immune involvement.
Topical Corticosteroids: These help reduce inflammation and scaling.
Medicated Shampoos: Coal tar and salicylic acid are common ingredients to break down thick plaques.
Systemic Therapies: For moderate or severe cases, a doctor may recommend biologics, immunosuppressants, or phototherapy.
Self-Care: Managing stress, moisturizing the scalp, and gentle cleansing are essential supportive measures.
Related Conditions to Be Aware Of
Understanding how scalp eczema vs psoriasis compares to other similar conditions can aid in proper diagnosis.
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis
Seborrheic dermatitis, a form of eczema, causes flaky scales often accompanied by oily skin. It’s common in areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Flakes are finer, greasy, and yellowish; borders are usually less defined.
- Psoriasis: Scales are thicker and drier, often with well-demarcated borders.
Dermatitis vs Psoriasis
Dermatitis is a general term for inflammation of the skin and includes many forms such as allergic contact dermatitis and irritant dermatitis.
Psoriasis: Caused by immune system overactivity; presents as well-defined plaques.
Dermatitis: Caused by irritants or allergens; presents as diffuse inflammation, often with blisters.
Scalp Eczema or Psoriasis: Which One Do You Have?
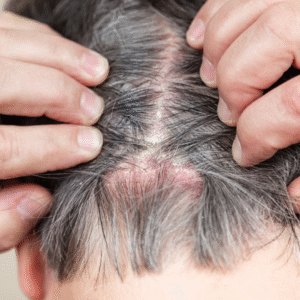
If you’re experiencing an itchy, flaky scalp, it’s essential to differentiate between scalp eczema vs psoriasis for effective treatment. Here are a few clues that might help:
- Does it itch intensely, especially at night? Likely eczema.
- Are the patches thick, raised, and scaling beyond the hairline? Likely psoriasis.
- Is your scalp greasy with yellowish flakes? Could be seborrheic dermatitis.
- Do you have other signs, like nail changes or joint pain? Consider psoriasis.
The best course of action is to consult a dermatologist. A professional can assess the specific characteristics of your scalp condition, perform any necessary tests, and provide a personalized treatment plan. Misdiagnosis or delayed treatment may worsen symptoms, so early evaluation is key.
Conclusion
Though they share overlapping symptoms, the distinctions between scalp eczema vs psoriasis are important for proper diagnosis and treatment. From appearance and sensation to underlying causes and therapies, knowing the differences empowers you to make informed decisions about your skin health.
If you’re struggling with scalp irritation and unsure of the cause, speak to your healthcare practitioner today.
References
Medical News Today: Scalp Eczema vs. Psoriasis: Pictures, Differences, and Treatment
WebMD: Psoriasis vs. Eczema: How to Tell the Difference
National Eczema Association: Is It Eczema or Psoriasis?
Mayo Clinic: Scalp Psoriasis vs. Seborrheic Dermatitis: What’s the Difference?
Canadian Dermatology Association: Article: Psoriasis vs. Eczema
