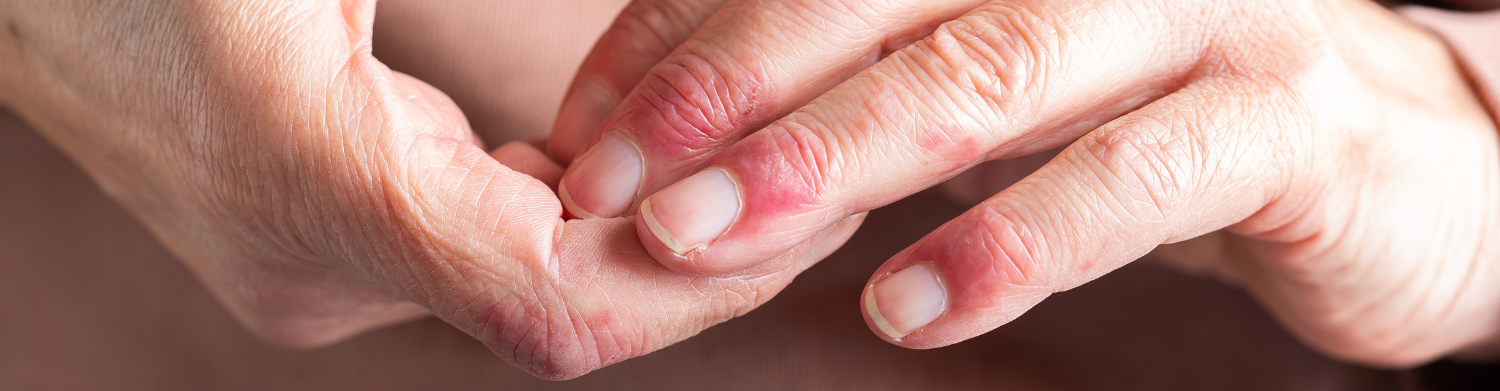
The Impact of Atopic Dermatitis on the Hands: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Symptoms | Differences | Management | Moisturization | Eczema Connection
The Impact of Atopic Dermatitis on the Hands: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Atopic dermatitis, often known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It affects millions of people worldwide and can impact various areas of your body. This condition can be particularly distressing when it affects your hands. During the day, your hands are constantly exposed to the environment and can become dry, cracked, and painful. With atopic dermatitis, you may experience intense itching, redness, and swelling on your hands.
In severe cases, your skin may become thick and scaly, making it difficult to move the hands and perform everyday tasks. There is currently no cure for atopic dermatitis. But there are treatments and therapies that can help relieve your symptoms. Common treatment options for atopic dermatitis include emollients, corticosteroids, and recently, probiotics.
Atopic Dermatitis on the Hands and Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Differentiating the Two
Atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis are two common types of skin conditions that can affect your hands. They also share some similar symptoms. It is important to differentiate between the two so you can create an effective treatment plan.
Atopic dermatitis typically causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma or hay fever as a part of the atopic triad. Stress, certain foods, or environmental factors can trigger atopic dermatitis flare-ups.
On the other hand, allergic contact dermatitis is a type of skin rash that develops as a result of exposure to an allergen or irritant. The symptoms may include redness, itching, and blistering. With allergic contact dermatitis your rash may be localized to the area where the allergen or irritant touched your skin.
The treatment for allergic contact dermatitis involves identifying and avoiding the allergen or irritant. You may even have to use topical or oral corticosteroids. If you are experiencing symptoms on your hands, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help determine the appropriate treatment plan for your condition.
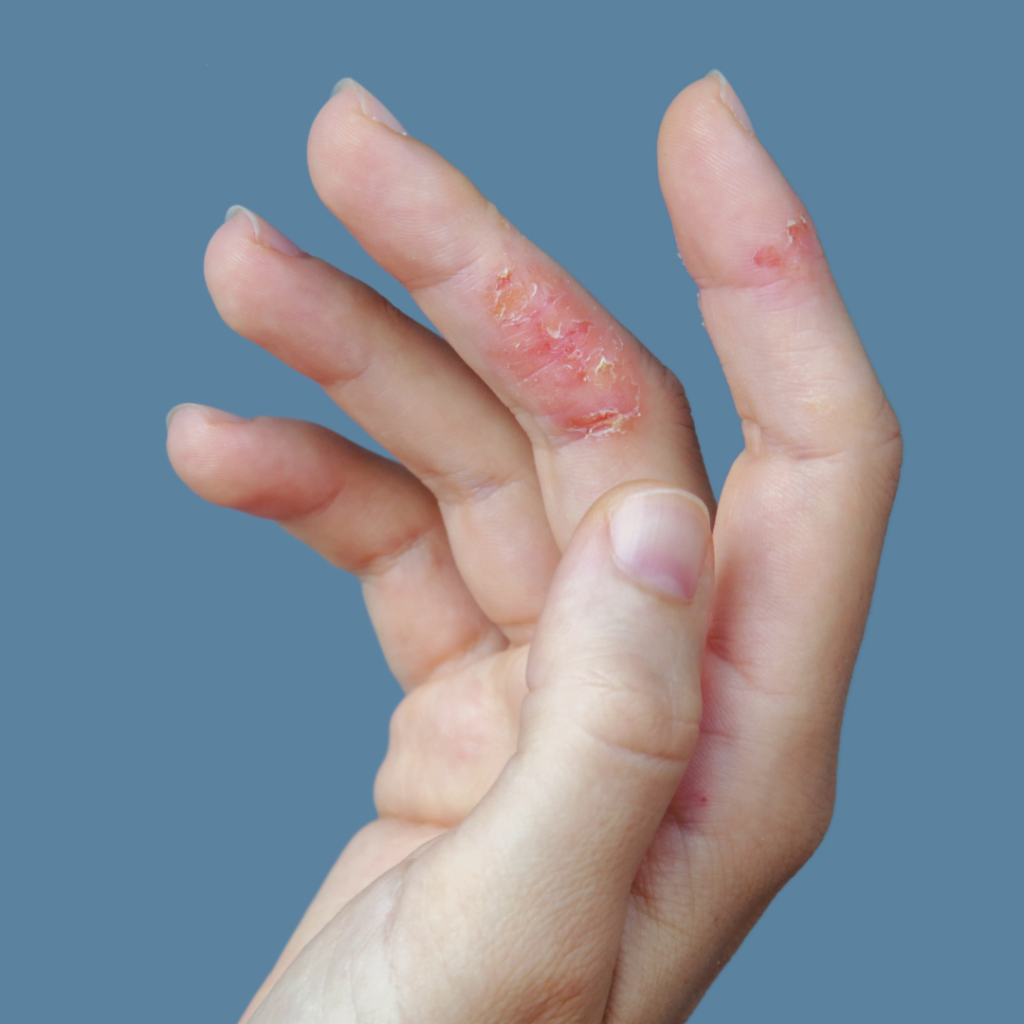
Managing Atopic Dermatitis on the Hands: Tips and Tricks
While it can occur anywhere on the body, the hands are a common location for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. This is because they are frequently exposed environmental irritants and washed. There are several tips and tricks that can help manage atopic dermatitis on your hands:
- Identify out what things make your skin feel worse, like using strong soap or cleaning products, and try to avoid them
- Use moisturizer often to keep your skin feeling soft and not dry
- Wear gloves when you’re cleaning or washing dishes to help protect your hands from irritants
If you have atopic dermatitis on your hands, it is recommended you work with a dermatologist to make a treatment plan. Your dermatologist or family doctor can curate management options that fit your lifestyle and needs.
The Role of Moisturizing in Treating Atopic Dermatitis on the Palms
Moisturizing is a important part of managing atopic dermatitis on your palms. It helps to restore the skin’s natural barrier, which is often compromised in people with eczema. When your skin is properly hydrated, it is less likely to crack and become inflamed.
Choosing the right moisturizer is also important. Look for products that are free from fragrance, dyes, and other potential irritants. Creams and ointments may be more effective than lotions because they are thicker. This may provide a better barrier to prevent moisture loss.
Apply moisturizer frequently throughout the day, particularly after washing your hands or taking a bath or shower. You may also want to skip hot showers and use lukewarm water instead. This can help stop your skin from drying out.
Exploring the Link Between Atopic Dermatitis and Hand Eczema: Understanding the Connection
Atopic dermatitis and hand eczema are two skin conditions that can cause significant discomfort and distress. While they may appear to be distinct conditions, there is a strong link between the two. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. Hand eczema specifically affects the hands and can cause redness, blistering, and cracking, similar to atopic dermatitis. Both conditions also share common risk factors. Family history, stress, and environmental triggers all play a part in atopic dermatitis and eczema.
If you have atopic dermatitis, you may get hand eczema more easily. Your skin barrier may be compromised leading to irritation from daily activities. Whether you have atopic dermatitis or eczema on your hands, it is recommended you talk to your healthcare provider. There are many ways to manage your symptoms and even newer ways of reducing the severity of your flare-ups naturally.
References
Eucerin: Atopic Dermatitis on the hands – The causes, symptoms and how best to calm and care for skin
National Eczema Society: Hand eczema
National Eczema Association: Hand Eczema
Mayo Clinic: Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
DermNet: Atopic hand dermatitis
